17 KiB
Hartman Lab Server Manual
© 2021 Bryan C. Roessler
Last updated: 2021-10-22
Table of Contents
- Important information
- For users
- For administrators
- Resources
- Contact
Important information
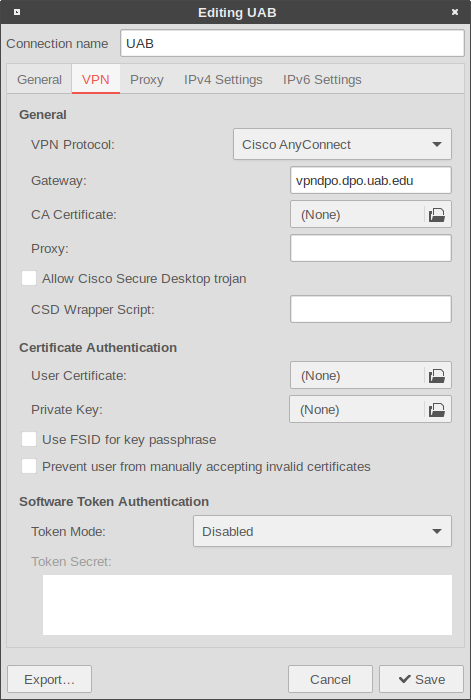
If UAB restricts direct ssh access to the Hartman Lab Server, users will need to first connect to the UAB VPN using the UAB AnyConnect VPN. Once the VPN connection is established, follow the rest of the manual to connect to the server.
For users that do not have UAB VPN credentials, a whitelist exception for the user's IP address will need to be added to the UAB firewall. Requests to UAB IT can be made here using your UAB credentials, and should resemble the following:
Type: Permit
Application Name: ssh
Firewall: UAB Internet Border
Source IP Addresses: User address(es)
Destination IP address: 138.26.17.151
TCP Port: 22
UDP Port: N/A
Other Protocols: N/A
Reason: Outside collaboration/(Other reason)
For users
First time login
- Ensure admin has enabled your user account.
- Login via ssh client (ssh or PuTTY):
ssh username@hartmanlab.genetics.uab.edu - Default password is identical to the
username - System will prompt you to create a new password
- System will log user out after successful password generation
- Re-login:
ssh blazerid@hartmanlab.genetics.uab.eduusing the new password - Optional: Change Samba password (default password is your username):
smbpasswd
File server
SSH/SFTP
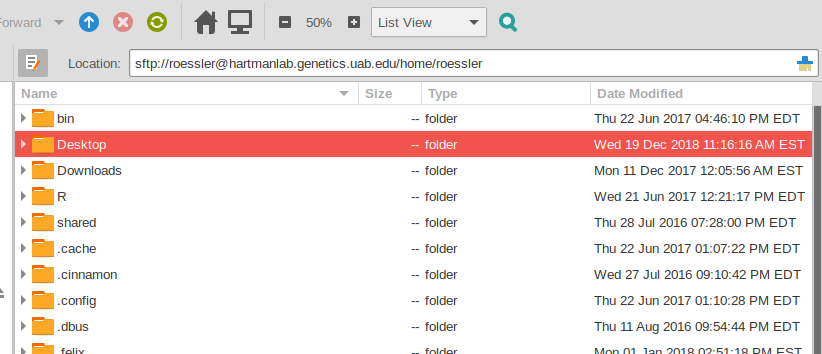
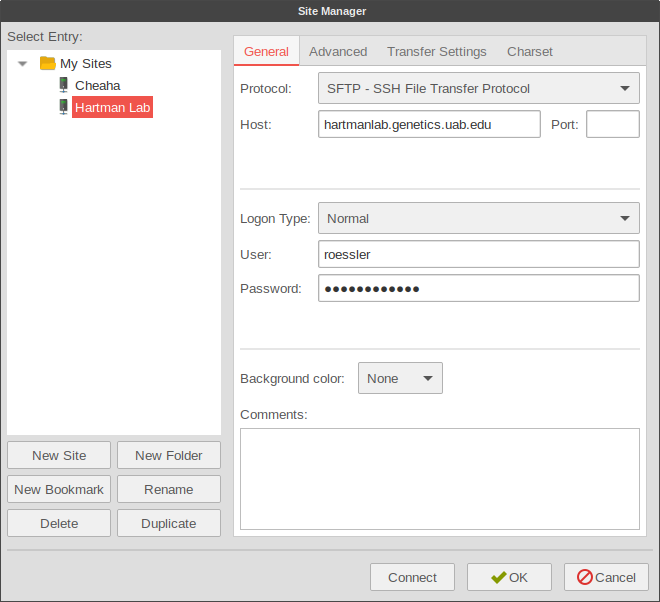
Files can be transferred to/from the server using sftp.
Users can access the server directly through a terminal (text-based) ssh client (ssh in OSX/Linux, or PuTTY in Windows) or via a GUI SFTP program such as Filezilla or WinSCP. Linux users can access and mount the SFTP share directly within most file managers or by using sshfs.
-
Using Filezilla to access sftp shares:
Samba file shares
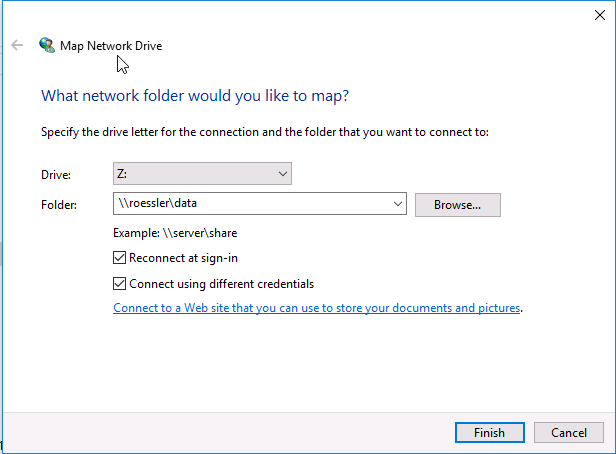
Samba file shares can be mounted cross-platform as if the data existed locally. The server provides two shares:
- The shared data array (
/mnt/data):\\username\data - The user's home directory (
$HOME):\\username\username
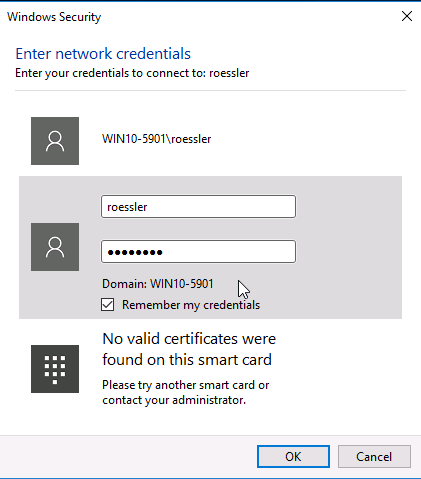
The default Samba credentials are the same as your server username and password. Users can change their Samba password using smbpasswd.
X2Go remote desktop
X2Go provides a remote virtual desktop over vnc secured with ssh. X2Go clients are provided for Windows, OSX, and Linux systems on the X2Go website or from your package manager (x2goclient).
X2Go sessions can be paused or closed from the X2Go client window. Multiple sessions can be saved in the client, making it easy to select alternate quality settings based on location/bandwidth or to provide multiple user login sessions on the same machine.
Note: Some programs do not continue to run at full speed when an X2Go session is paused. In these cases, the program should be run via remote SSH (ideally in a tmux or screen session).
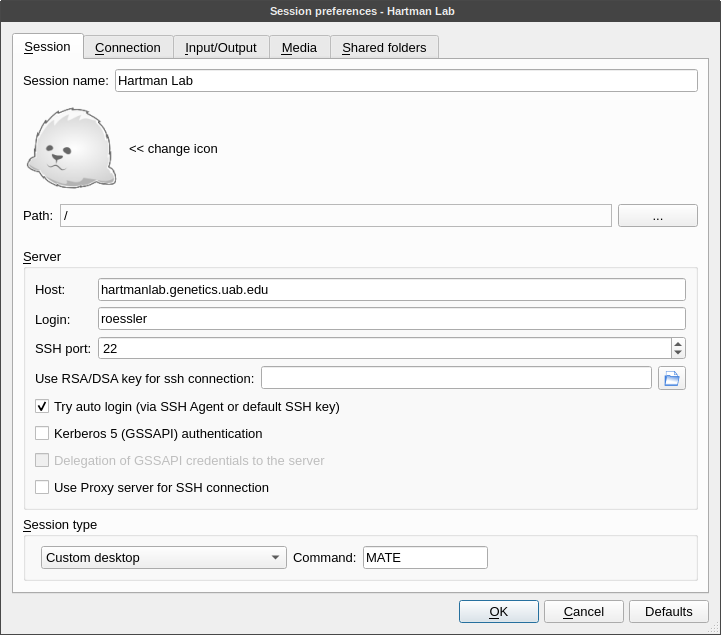
Session tab
-
Session name: Hartman Lab Server
-
Host: hartmanlab.genetics.uab.edu
-
Login: username
-
SSH port: 22
-
Session type: MATE (Not all session types are allowed and MATE should provide the best experience with X2Go)
Connection tab
- Set the connection speed to LAN when connecting from within the UAB network. When connecting from off-campus these quality values can be adjusted based on bandwidth and latency.
- Compression settings should be left unchanged or set to adaptive.
Input/output tab
- If automatic window resizing is not working properly (common on HiDPI monitors), set the desired startup window resolution size manually. For fullscreen sessions, this should match your client display.
- If there are any issues with keyboard mapping (ex. the arrow keys are not working), select Configure Keyboard and leave the default selected settings.
Media tab
Disable sound support. This will prevent pulseaudio from spamming the server logs.
Shared folders
- Select folders on the client to be shared with the server during a session. Browse to the chosen folder, add it to the share, and select automount.
- These folders will then appear on the server under
/media/disk/<share_name>.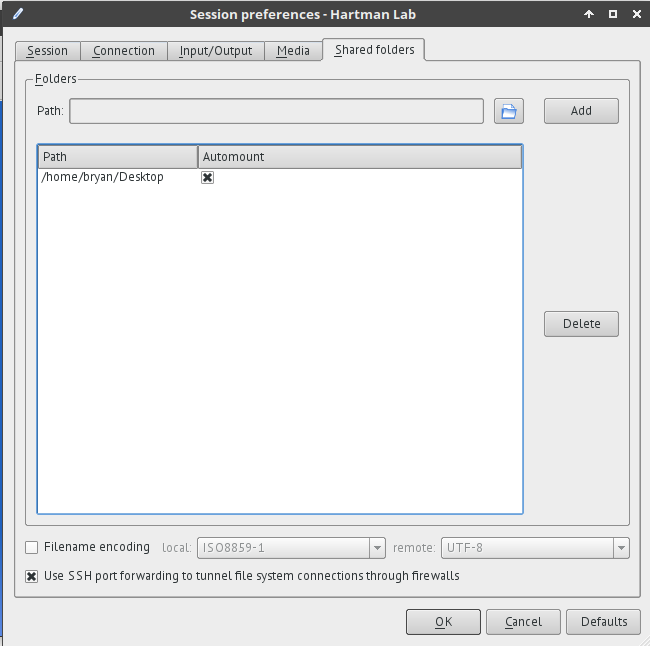
Native X forwarding
It is possible to launch graphical server programs directly on a client.
Linux, OSX
ssh -X username@hartmanlab.genetics.uab.edumatlab(to launch Matlab GUI on the client)
Windows
Windows 10 Virtual Machines
-
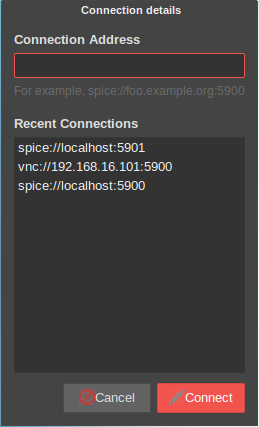
Access from within X2Go: Applications>Internet>Remote Viewer:
spice://localhost:5900 -
Direct external access:
virt-vieweris available across all platforms (Windows, OSX). -
The SPICE password is:
hartmanlab
The virtualized Windows 10 instances require logging in with your UAB email address and password.
- Note: Users should NOT log in with a pin when prompted, it will disable access to the Samba file shares (Windows bug). Users should always log in with a password.
Once you are finished using the Windows virtual machine, remember to log out of your UAB Windows account so that other users do not have access to your session. Windows will perform an automatic logoff after 30 minutes of inactivity for security.
Robot computer access
- While logged into the server, launch Applications>Internet>Remote Viewer>Connection>New:
vnc://192.168.16.101:5900
Webcam robot monitoring
The robot webcam is viewable in a web page within an X2Go session at: localhost:8888
RStudio Server
Newer versions of RStudio do not support IDE access via X2Go. The IDE can be accessed via web browser at http://localhost:8787 in an X2Go session or via an SSH tunnel, ex. ssh -f username@hartmanlab.genetics.uab.edu -L 8787:localhost:8787 -N
Recommendations
Backing up data
The rsync, rsnapshot, and syncthing tools are installed on the server to facilitate user backups.
rsync is recommended for users that would just like to periodically backup their $HOME directory to a local machine over ssh:
rsync -azH --delete username@hartmanlab.genetics.uab.edu:~/* ~/backup/
A GUI alternative, syncthing (Applications>Internet>Syncthing) syncs folders and files between machines automatically and is accessible at http://localhost:8384
Passwordless (public-private key) authentication
Public-private key authentication is more secure than passwords and can be configured for passwordless login.
- Generate the key-pair and add it to the server:
- To enable public-private key authentication, the user will need to generate a public and private keys on the client machine using
ssh-keygen(Linux & OSX) orPuTTYgen(Windows). The user can then transfer the public key to the server usingssh-copy-id.
- To enable public-private key authentication, the user will need to generate a public and private keys on the client machine using
- Configure the X2Go client for passwordless login:
- Linux
- Check the Try autologin box in the session settings.
- OSX/Windows
- Select Use RSA/DSA key for ssh connection in the session settings and select the location of the public key manually.
- Linux
Most popular SFTP programs support using public-private keys for passwordless authentication. Windows/OSX users may need to add their key pair to PuTTy/Filezilla/WinSCP manually.
Once configured, the user will no longer need to enter their password to access the SFTP or X2Go server, which simplifies login and enhances security.
For administrators
- Type
scripts-and usetabcompletion in the CLI to access the following customized helper programs. - Run them with administrator privileges using
sudo.
Adding a user
script-user-addusernamepassword- Optionally pass a second argument
passwordto create a user's password for them. If omitted, the default password is equal to theusername. usernamecan be anything, but ideally a unique string of small capital letters.
- Optionally pass a second argument
Resetting a user password
script-user-reset-passwordusernamepassword- If a user forgets their password this will reset it to
password, or ifpasswordis omitted, to theusername. In either case the user will be prompted to enter a new password at next login. The Samba password cannot be changed by users, only admins.
- If a user forgets their password this will reset it to
Removing a user
script-user-removeusername- This will allow you to optionally backup user files to the array before user deletion.
Reset a buggy or corrupt X2Go user session
script-user-reset-x2gousername- Completely reset the X2Go state for the user
username. This will destroy any active or paused X2Go sessions for that users.
- Completely reset the X2Go state for the user
Unban a user
script-user-unbanIP Address- Fail2ban is configured to whitelist the UAB subnet, however repeated failed authentication attempts from off-campus clients will result in a compounding “cool down” period starting at 10 minutes where repeated login attempts from an IP address will be blocked. In cases of emergency, this can be reset manually if the user provides their WAN IP address.
Fix or repair user file permissions
script-files-permissions-setusernamepasswordPATH[...]- This script will walk you through fixing or setting the permissions on one or more
PATH's. If no PATH is provided the$PWDis used.
- This script will walk you through fixing or setting the permissions on one or more
script-files-permissions-resetPATH[...]- If no
PATH[...]is provided it will reset the data array/mnt/data. - If things go really south, use this script as a method of last resort to reset permissions on a path by resetting the original permissions for the shared data.
- If no
Services
- Start:
sudo systemctl start smb.service - Stop:
sudo systemctl stop smb.service - Enable at boot:
sudo systemctl enable smb.service - Disable at boot:
sudo systemctl disable smb.service - Restart service:
sudo systemctl restart smb.service - Reload services:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload - Read service:
sudo systemctl cat smb.service
Virtual Machines
-
Use
virt-managerto create a new virtual machine- Optionally copy an existing Windows
.qcow2image so that Windows and the virtio drivers do not need to be reinstalled. - In case a new VM is required, the Windows virtualization drivers (
virtio) are located at/usr/share/virtio-win.
- Optionally copy an existing Windows
-
Activate Windows using the UAB license in elevated Powershell:
slmgr -skms itis-msls.ad.uab.edu slmgr -ato -
Add the UAB DNS server(s) (138.26.5.2, 138.26.5.66) to the Windows network config access UAB resources
Allow access to the samba share within the Windows VM (Windows bug workaround)
- Open
C:\Windows\system32\drivers\etc\hostsfile and copy contents. - Open new text document, paste contents of existing hosts file and add appropriate blazerid and server IP line (see existing entries).
- Save as “hosts” (no extension).
- Copy new hosts file to
C:\Windows\system32\drivers\etc\(allow it to overwrite existing hosts file). - The new user will be able to map/access their samba shares at
\\blazerid\dataand\\blazerid\blazerid.
Make an existing Windows 10 account user an administrator
- Login to the PC as the Azure AD user you want to make a local admin.
- Log out as that user and login as a local admin.
- In elevated Powershell, add the user to the administrators group:
net localgroup administrators AzureAD\\blazerid@uab.edu /add
Creating more VM disk space
- Add 20 GBs of space to the Windows VM:
sudo qemu-img resize /var/lib/libvirt/images/win10-5900.qcow2 +20G - Add gparted iso as boot device and expand working partition.
Updating system software
script-system-update- The server regularly installs security updates unattended
- If the kernel, java, systemd, or other major components are updated, the system should be restarted.
Updating RStudio and RStudio Server
-script-system-update-r
Scheduling a restart
script-system-scheduled-restartOnCalendar- If a valid
OnCalendaris not passed, assumes*-*-* 01:30:00(1:30 AM). - See Calendar Events for time formatting.
- This will alert users via
notify-sendin X2Go,wallin ssh, and add a reminder to themotdabout the scheduled restart.
- If a valid
Adding a drive
scripts-drive-add/dev/sdX- To determine the correct drive, use
lsblk -f.
- To determine the correct drive, use
Logging
- First point of reference for server problems:
sudo journalctl- Follow new output:
sudo journalctl -f - Reverse logs:
sudo journalctl -r
- Follow new output:
- Logging in via
sshwill provide some useful server information in themotd.